The trigger points in the next three muscles cause a temple
headache, which may be a typical experience of a migraine headache.
1) splenius cervicis (SPLEE-nee-us SUR-vuh-sis)
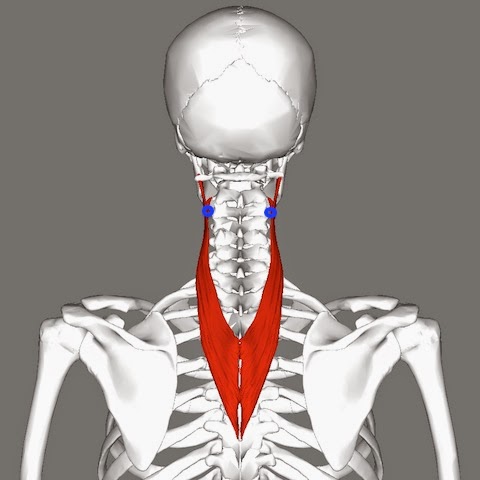 |
| splenius cervicis |
It is different from the splenius capitis mentioned in the crown headache. The splenius cervicis doesn’t attach to
the skull, but connect the vertebrae of the upper back to those of the
neck. The trigger point in the
upper muscles indicated in the blue circles causes the pain coming from the base of the skull, through the
head to the back of the eye. It
feels like throbbing pain inside the skull.
2) suboccipital (sub-ahk-SIH-pih-tul) muscles
 |
| suboccipitals |
They consist of four small muscles on each side of the base of the
back of the skull (occipital bone). If you move your head frequently,
contract these muscles too long, or have emotional tension, you get trigger
points in these muscles indicated in the black circles and and referral pain in the back of the head to the eye and forehead. If you
have trigger points in the trapezius,
you tend to get trigger points in the suboccipitals, causing migraine.
3) semispinalis capitis (she-mee-spih-NAH-liss CAP-uh-tiss)
 |
| semispinalis capitis |
The muscles connect the vertebrae of the upper back and
lower neck to the base of the occipital bone. You can find trigger points anywhere along the muscles, but
the ones in the upper part of the muscles indicated in the blue circles are the cause of a band of pain around your head above the ear, which is similar to the referral pain pattern of suboccipitals.